Orthognathic surgery: one true story
[et_pb_section fb_built=”1″ _builder_version=”3.0.47″][et_pb_row _builder_version=”3.0.47″ background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat”][et_pb_column type=”4_4″ _builder_version=”3.0.47″ parallax=”off” parallax_method=”on”][et_pb_text _builder_version=”3.0.47″ background_size=”initial” background_position=”top_left” background_repeat=”repeat”]
The orthodontic-surgical course of Sindu
The best way to illustrate the orthodontic management of a case presenting the sequelae of a complete facial cleft (primary and secondary palate: complete unilateral cleft lip and maxillofacatine) is to do so with the help of a real-life example, followed along the course of and with sequelae that can be described as “typical” without forgetting that the problem is characterized by great variability: here is the course of SINDUH Sindhu was born with a complete cleft involving the lip, alveolar bone and palate on the left. Operated in India, then adopted by a family in Switzerland.
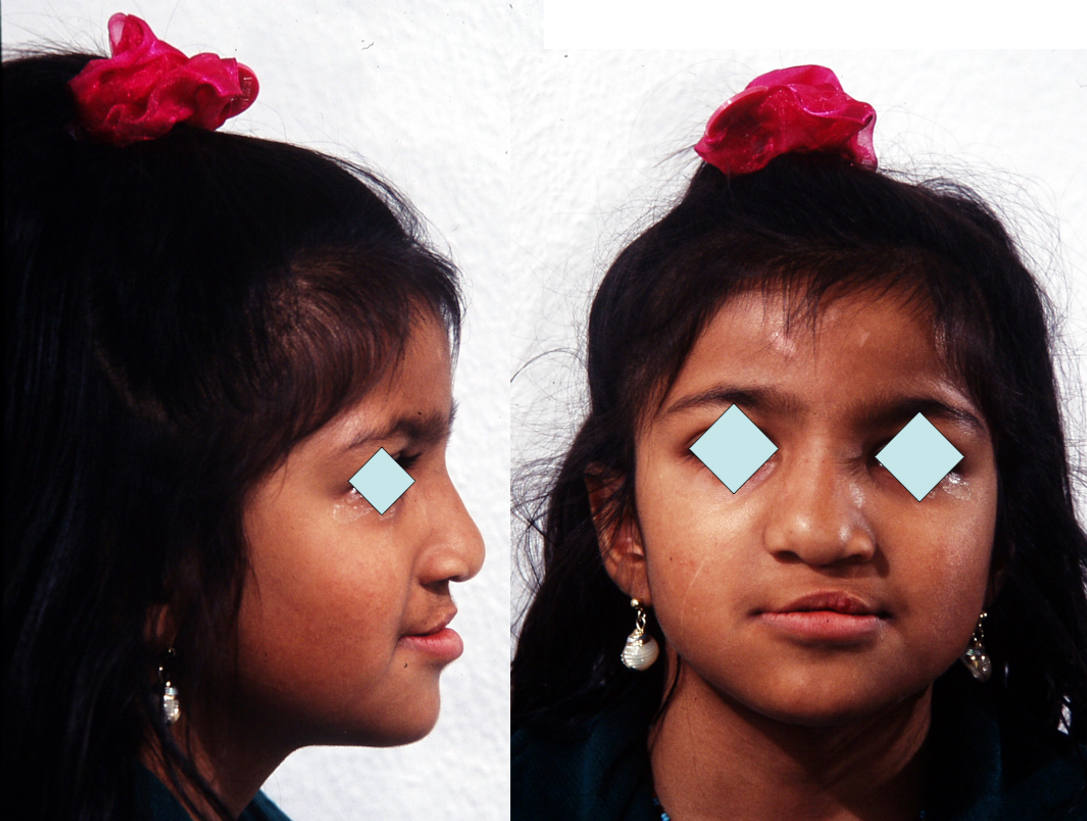

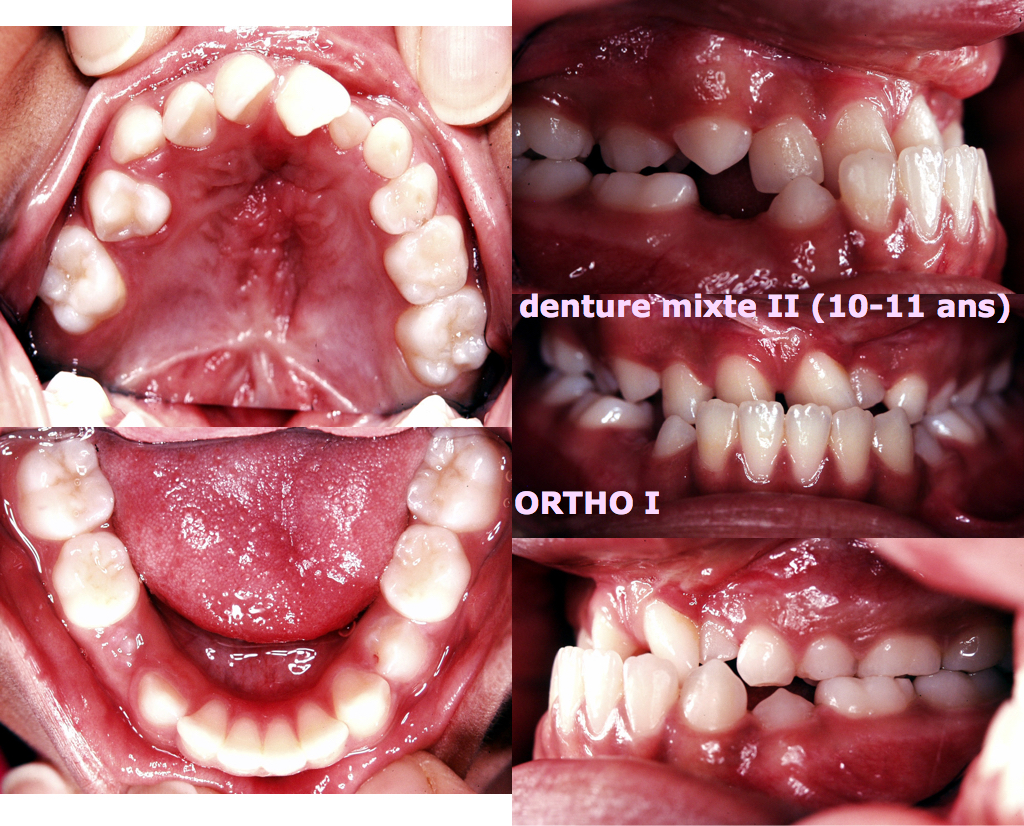
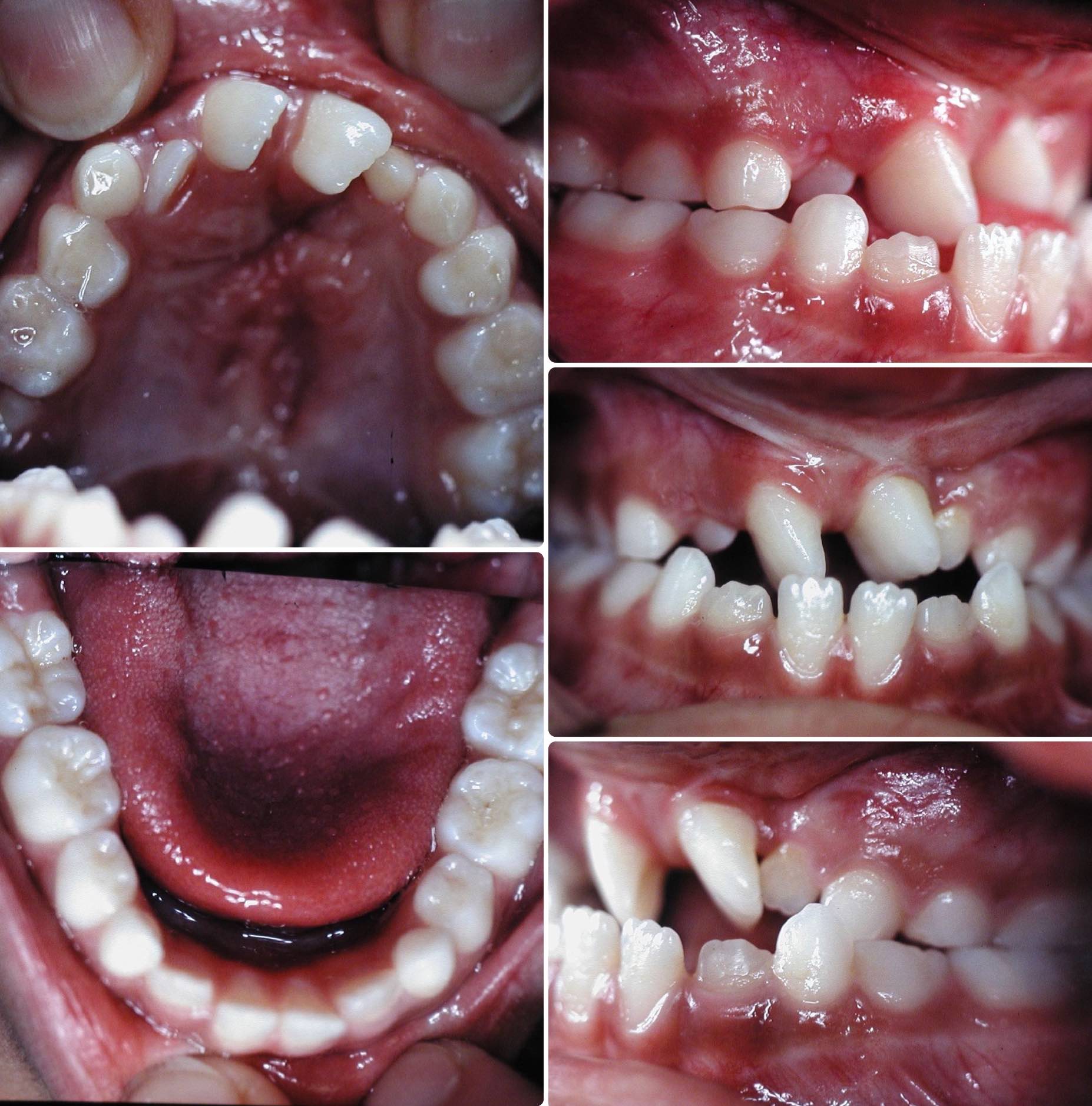 Fig 1. Mixed dentition stage (8.3 years) : severe malocclusion with:
Fig 1. Mixed dentition stage (8.3 years) : severe malocclusion with:
complete crossbite, which means that the upper dental arch is biting “inside“ the lower arch, being narrower and shorter.
rotation and severe malposition of the upper incisor teeth
the lower dental arch is basically normal.
-
-
The lateral incisor on the side of the cleft is absent (agenesis is frequently observed, around 76 to 80% of the time).It will be soon necessary to perform a bone grafting (Sindiu is now 8 years and 3 months old).
-
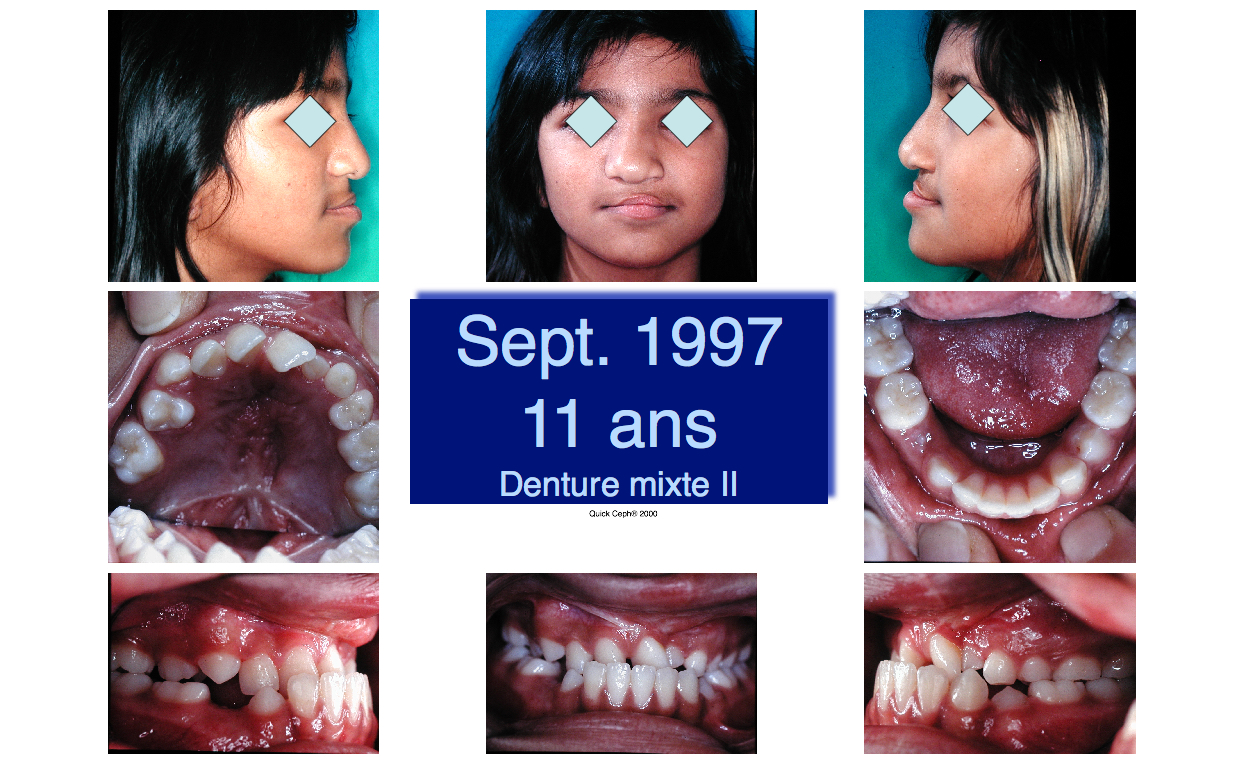
Fig 2. Lateral Xray showing a concave profile
Fig 3 & 4. End of the mixed dentition stage: most of the permanent teeth have erupted, save the left upper canine, the left lateral incisor and the second bicuspids and second permanent molars)
There is stil a crossbite and the profile is concave (retruded upper jaw).
The profile cannot be corrected and improved by orthodontic means only: a surgical intervention (Lefort I osteotomy) will need to be planned and performed. It will be performed at the end of the pubertal growth period and the teeth will have to be prepared for this intervention with the help of a full fixed appliance (braces).
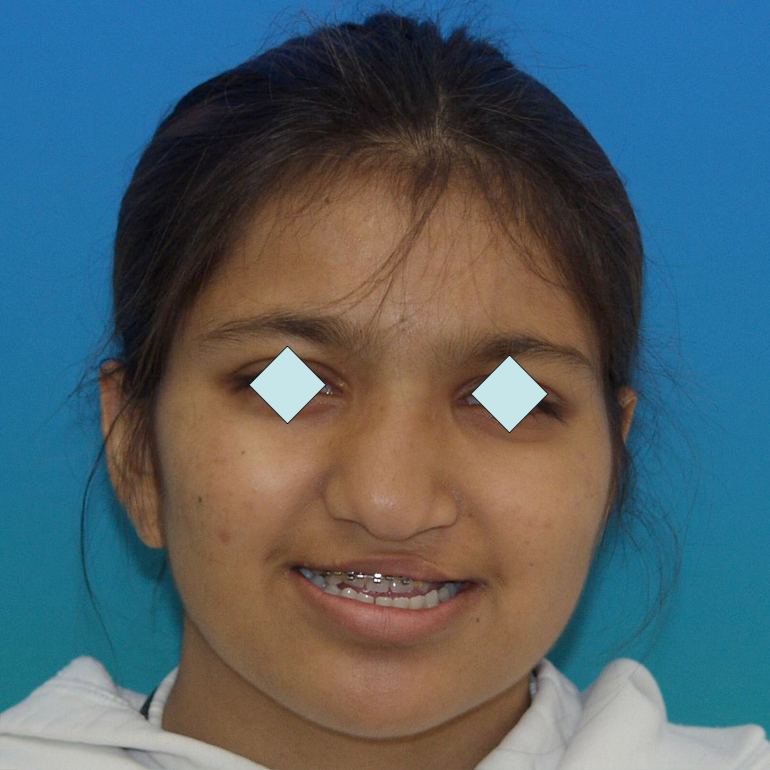
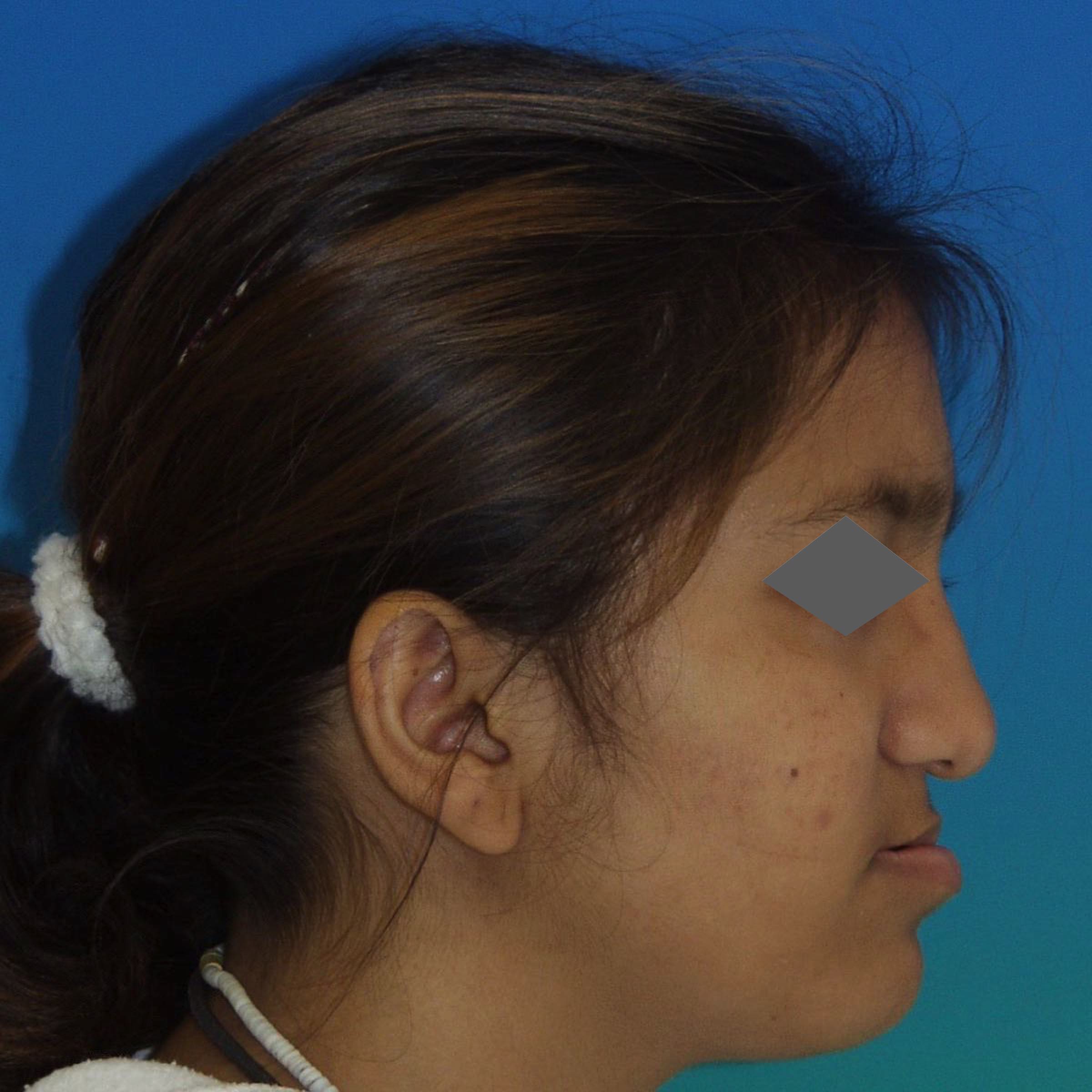
Fig 5 & 6 Extra-oral appearance before surgery
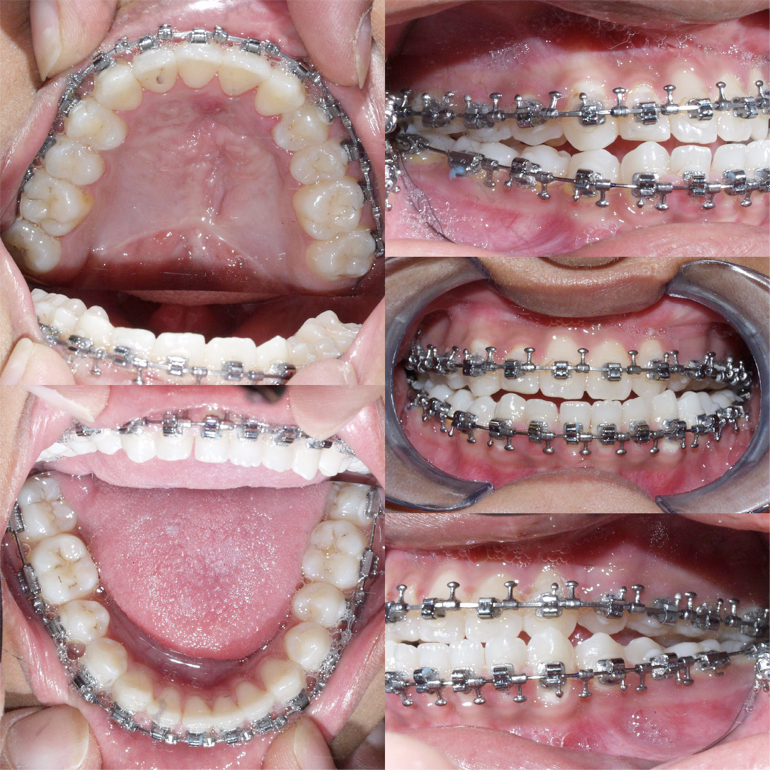 Fig 7 Presurgical orthodontic preparation
Fig 7 Presurgical orthodontic preparation
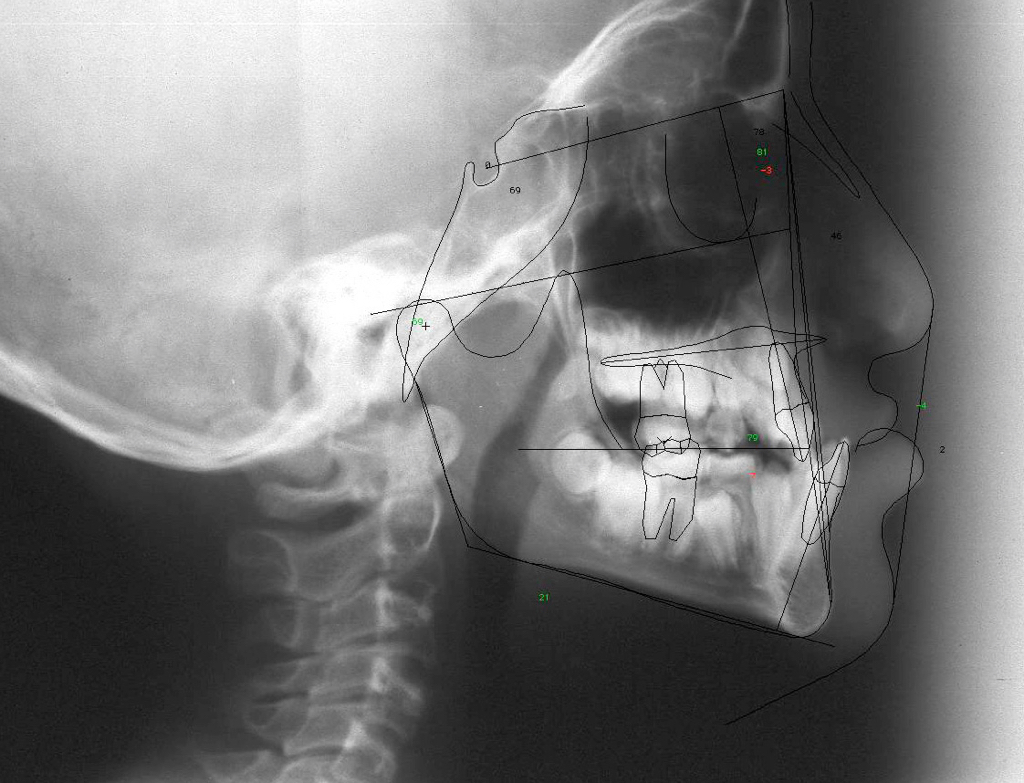
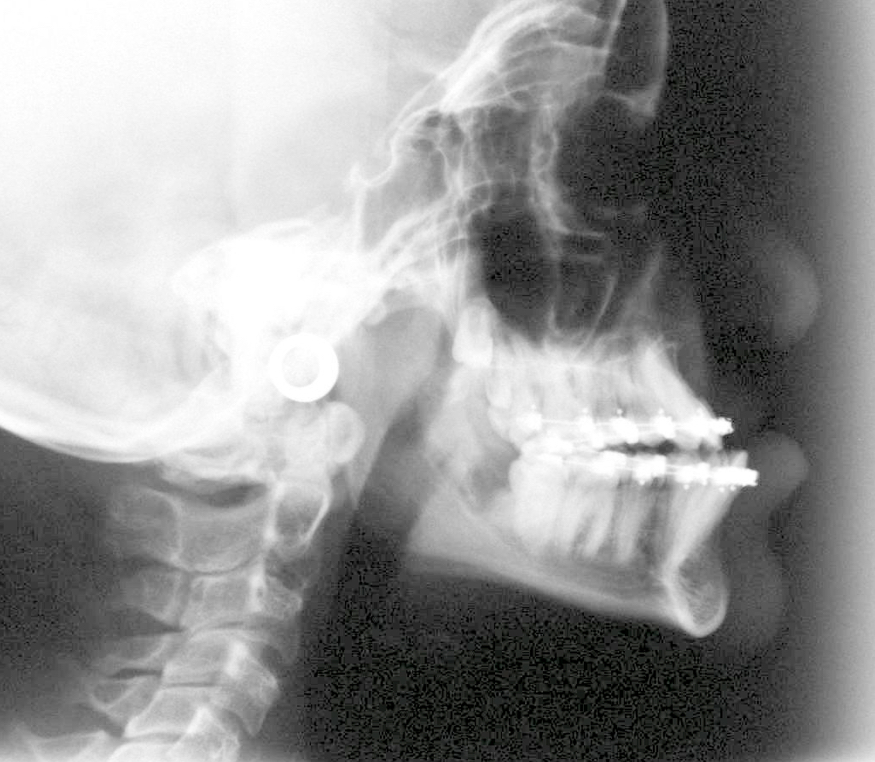 Fig 8 Lateral Xray showing the pre-surgical facial appearance (concavity of the profile)
Fig 8 Lateral Xray showing the pre-surgical facial appearance (concavity of the profile)
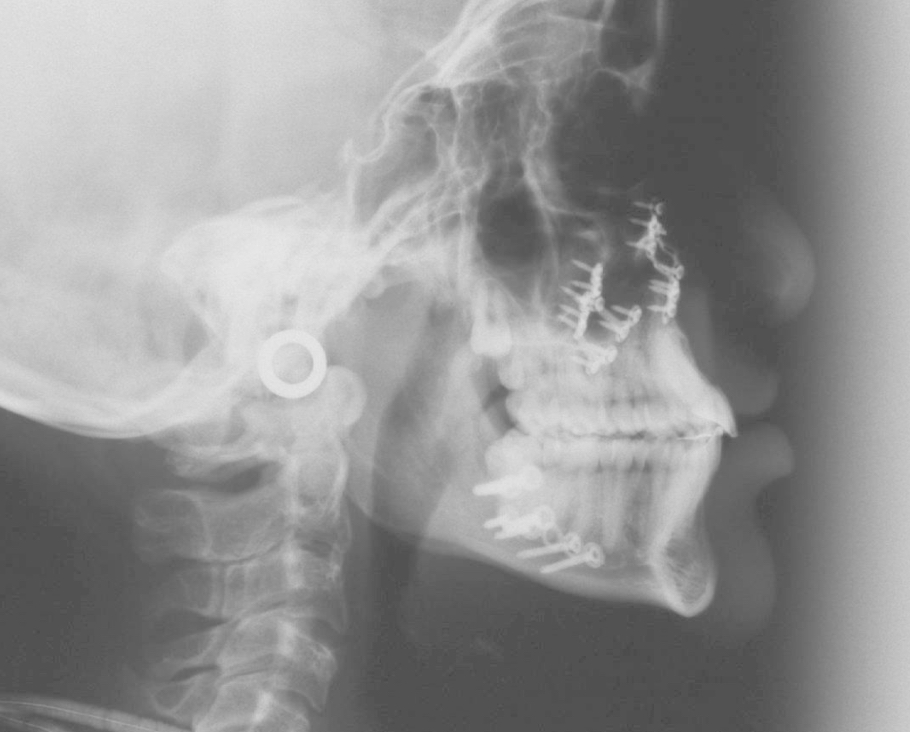
Fig 9 Lateral Xray showing the post-surgical appearance, after advancement osteotomy of the upper jaw and push-back of the mandible. Please note the screws and plates that serve as rigid fixation, The teeth are now in good relationship, esthetically as well as functionally.
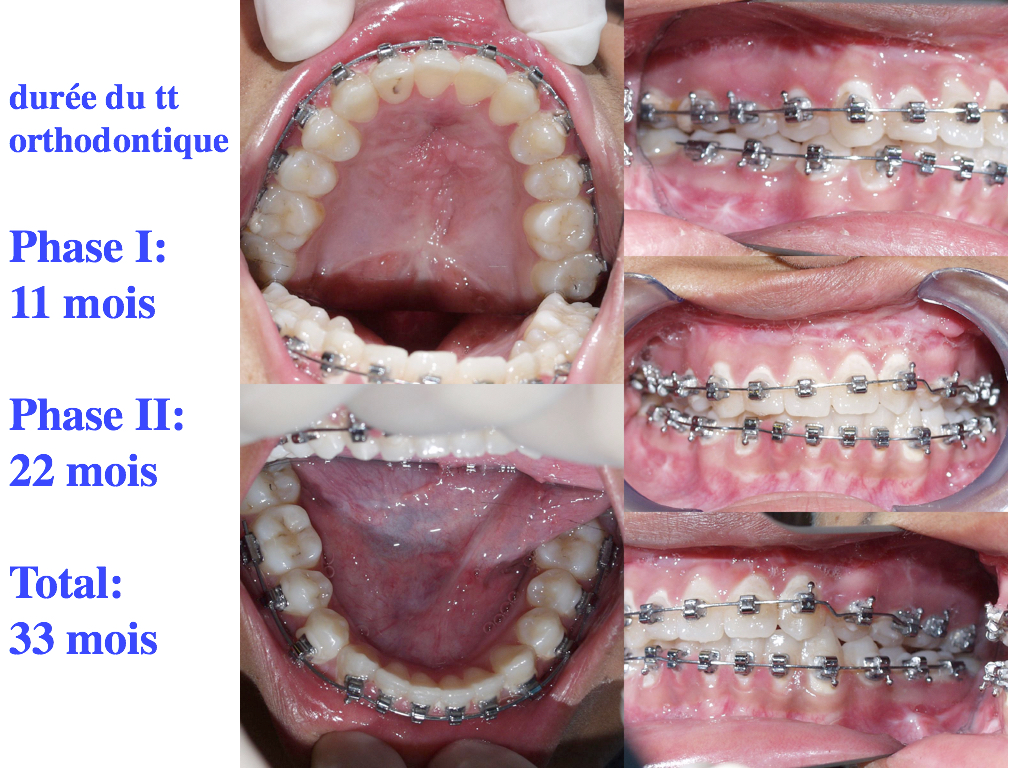
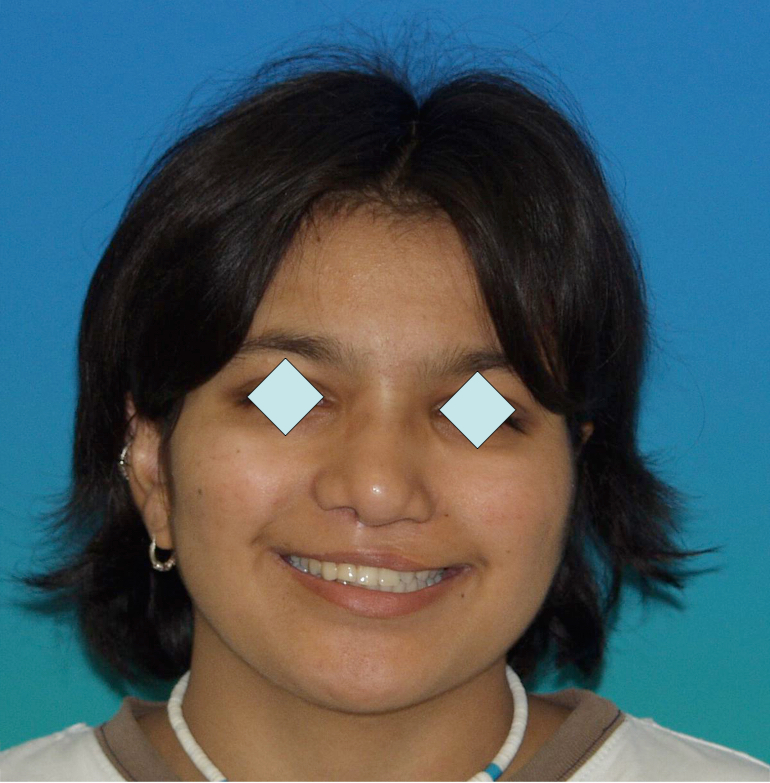
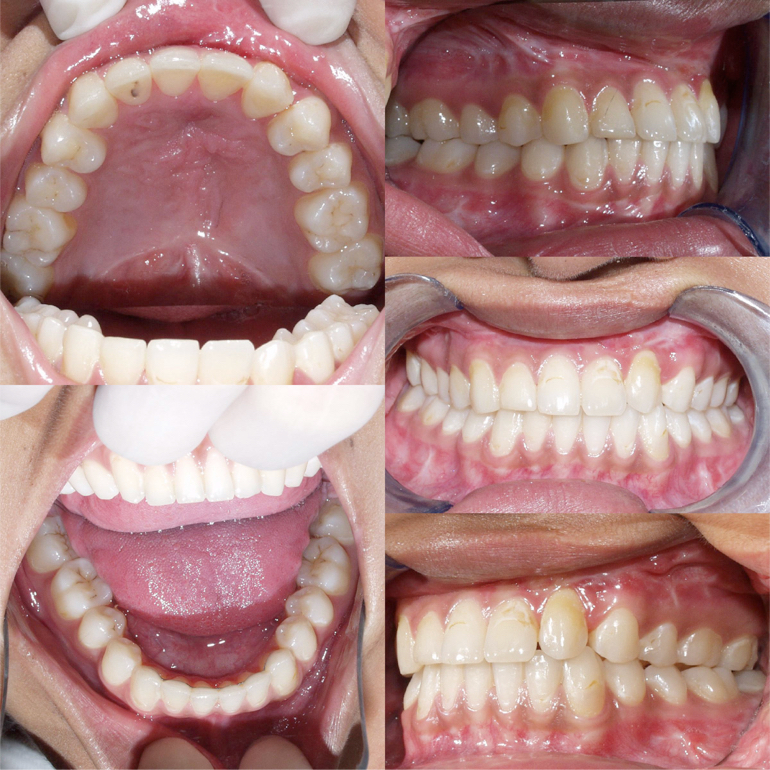 Fitg 10-11-12 Final result
Fitg 10-11-12 Final result
Georges Herzog, consultant orthodontist of the CLP teams of the CHUV (Lausanne) and HUG (Geneva), contact: info@cleft-palate.com
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]